Bone Grafting: Restoring Strength and Structure
Bone grafting is a remarkable medical procedure that plays a vital role in restoring bone strength and structure. It is a surgical technique used to repair and regenerate damaged or lost bone tissue, providing support and stability to areas affected by injuries, diseases, or other conditions. This advanced procedure has revolutionized the field of orthopedics and dentistry, enabling patients to regain mobility, function, and quality of life.
Understanding Bone Grafting:
Bone grafting involves the transplantation of bone tissue from one part of the body (autograft) or a donor source (allograft) to the affected area. The graft acts as a scaffold, promoting the growth of new bone cells and encouraging the natural healing process. Additionally, synthetic materials or bone graft substitutes derived from animals or synthetic sources may also be used in specific cases.
Indications for Bone Grafting:
- Fracture Repair: In cases of severe fractures with significant bone loss or damage, bone grafting aids in stabilizing the fractured bone segments and supporting their fusion for proper healing.
- Joint Reconstruction: For patients with joint problems like arthritis or joint degeneration, bone grafting can facilitate joint reconstruction, improving joint function and reducing pain.
- Spinal Fusion: In spinal surgeries, bone grafts are commonly used to fuse vertebrae together, addressing spinal instability and providing support to the spine.
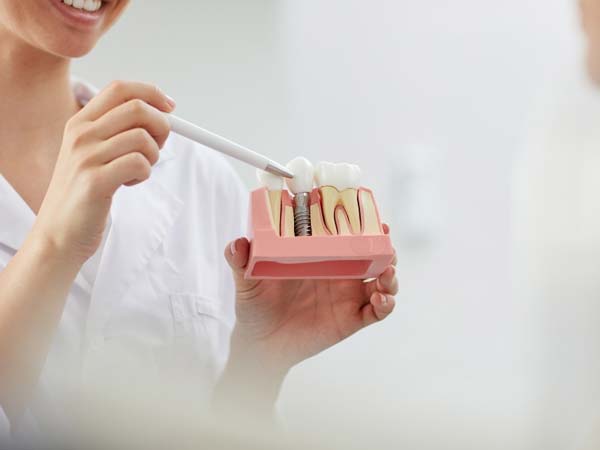
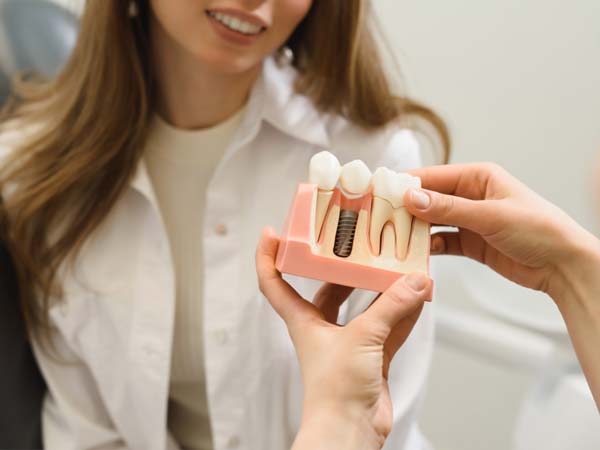
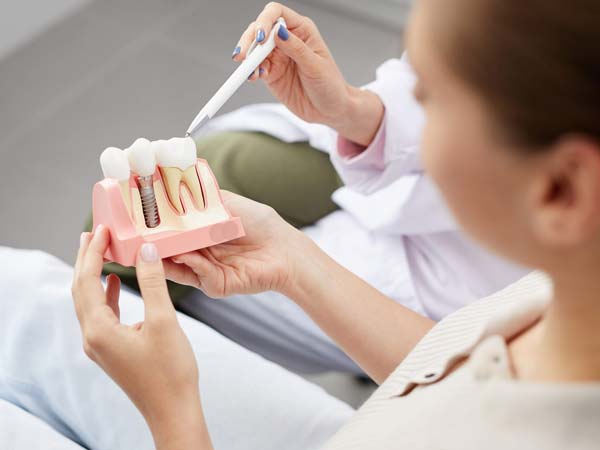
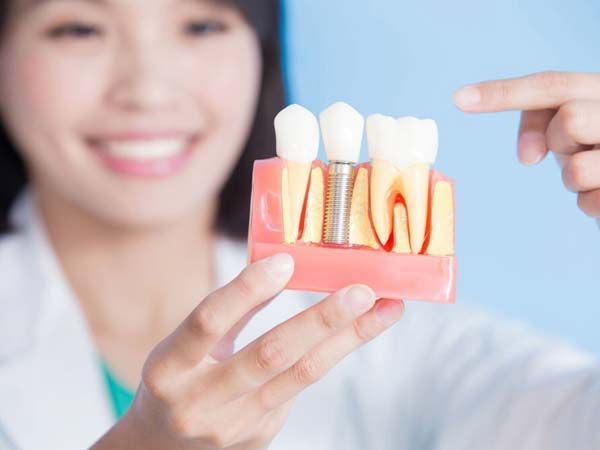
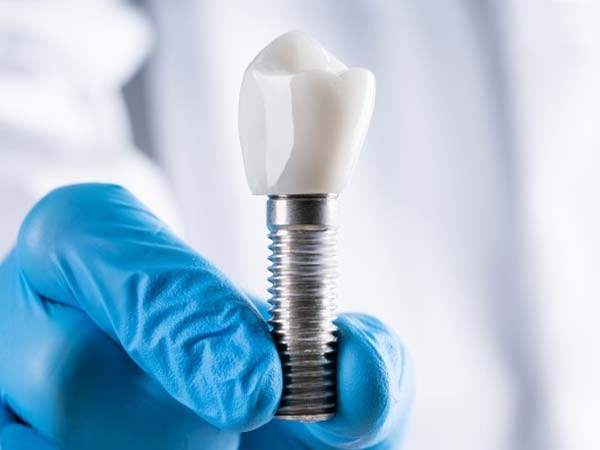
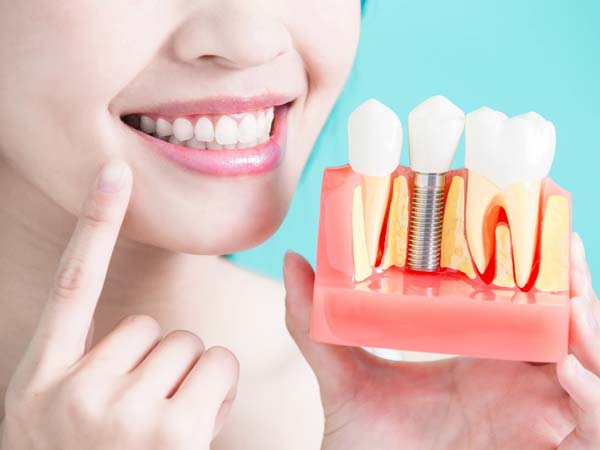
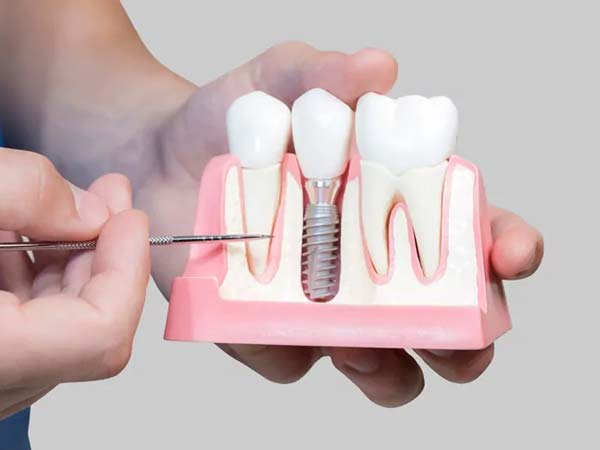
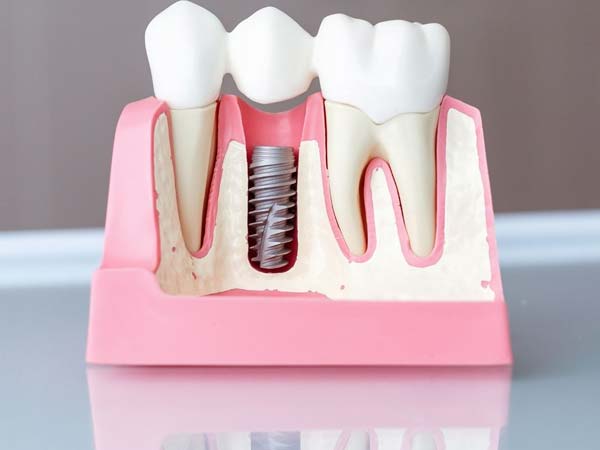
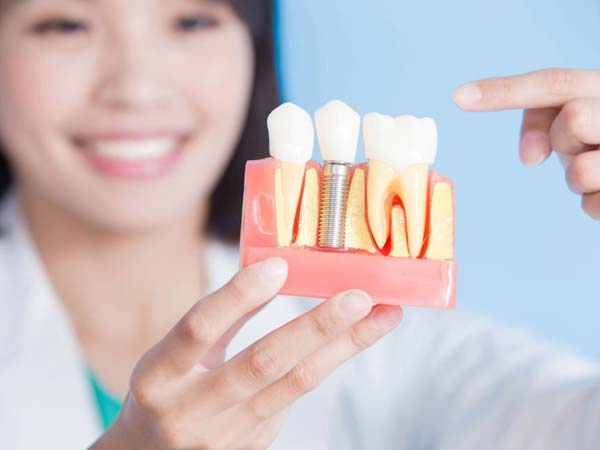
- Dental Implants: Dental bone grafting is utilized to enhance the density and volume of the jawbone, creating a strong foundation for successful dental implant placement.
- Corrective Surgery: Bone grafts are often used in corrective surgeries for deformities, non-unions, and malunions, restoring normal bone alignment and function.
Types of Bone Grafts:
- Autografts: These grafts are harvested from the patient’s own body, typically from areas like the hip, tibia, or ribs. Autografts are considered the gold standard due to their excellent compatibility and ability to promote bone healing effectively.
- Allografts: Allografts are obtained from cadavers or living donors and processed for surgical use. They offer a viable alternative when there is insufficient autograft material available.
- Xenografts: Xenografts involve the use of bone material from other species, often bovine or porcine sources. These grafts provide a scaffold for bone growth and are eventually replaced by the patient’s bone tissue.
- Synthetic Grafts: Synthetic bone graft substitutes, such as calcium-based materials or biocompatible polymers, offer a viable option for patients who cannot undergo autografting or allografting procedures.
Bone Grafting Procedure:
The bone grafting procedure is usually performed under anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort. The surgeon makes an incision at the treatment site and carefully prepares the area to receive the graft. The graft material is then placed, and the site is secured with screws, pins, or plates, depending on the case’s complexity.
Recovery and Healing:
Post-surgery, patients undergo a healing period where the bone graft integrates with the existing bone. The recovery time varies depending on the procedure’s complexity and the patient’s overall health. During this time, patients may need to follow specific post-operative care instructions, including restricted physical activity and maintaining good oral hygiene in dental bone grafting cases.
Advancements in Bone Grafting Techniques:
Medical science continuously evolves, and bone grafting procedures have seen significant advancements over the years. These advancements include the use of growth factors and stem cells to enhance bone healing, minimally invasive techniques that reduce recovery time, and the development of bioactive materials that encourage faster bone regeneration.
Consultation with a Specialist:
If you are considering bone grafting or have been recommended the procedure, it is crucial to consult with an experienced orthopedic surgeon, oral surgeon, or dental specialist. They will evaluate your specific condition, discuss the available treatment options, and provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs.
Conclusion:
Bone grafting is a remarkable surgical procedure that restores bone strength, promotes healing, and enhances overall function. Whether for fracture repair, joint reconstruction, spinal fusion, dental implants, or corrective surgery, bone grafting plays a pivotal role in helping patients regain their mobility and quality of life. With advancements in techniques and materials, this procedure continues to revolutionize the field of orthopedics and dentistry, offering new hope for patients in need of bone restoration.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Is bone grafting a painful procedure? During the procedure, patients are under anesthesia, so they do not experience pain. After surgery, mild discomfort or soreness is normal and can be managed with prescribed pain medication.
- How long does it take for a bone graft to heal? The healing time varies depending on the complexity of the procedure, the patient’s overall health, and the location of the graft. It can take several weeks to several months for the bone graft to fully integrate and heal.
- Are there any risks or complications associated with bone grafting? As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. These may include infection, bleeding, graft rejection, nerve damage, or insufficient bone healing. Your surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.
- Can anyone undergo bone grafting? Most individuals who require bone restoration can undergo bone grafting. However, it is essential to consult with a specialist who will evaluate your specific condition and medical history to determine if you are a suitable candidate for the procedure.
- 5. How long do the results of bone grafting last? The results of bone grafting are typically long-lasting. Once the graft has integrated with the existing bone, it becomes a permanent part of the body. However, maintaining good overall health and following post-operative care instructions are essential for optimal outcomes.