Periodontics: Maintaining Healthy Gums for a Strong Foundation
Periodontics is a specialized branch of dentistry that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases and conditions affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Healthy gums are essential for maintaining a strong foundation for your teeth, as they provide support and protection against harmful bacteria. Let’s explore the significance of periodontics and how it contributes to your overall oral health.
The Importance of Periodontics:
- Prevention and Early Detection: Periodontists play a crucial role in preventing gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis. They emphasize the importance of regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Early detection of gum problems allows for prompt treatment and prevents further progression of the disease.
- Treatment of Gum Diseases: Periodontists are experts in diagnosing and treating various gum diseases. They employ non-surgical and surgical techniques to eliminate infection, reduce inflammation, and restore gum health. These treatments may include scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), gum grafting, pocket reduction surgery, and guided tissue regeneration.
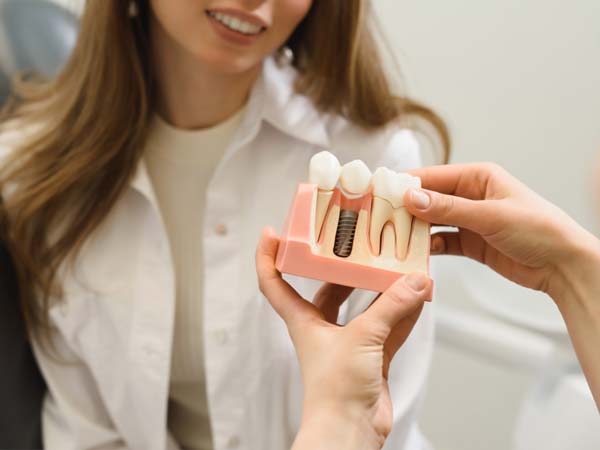
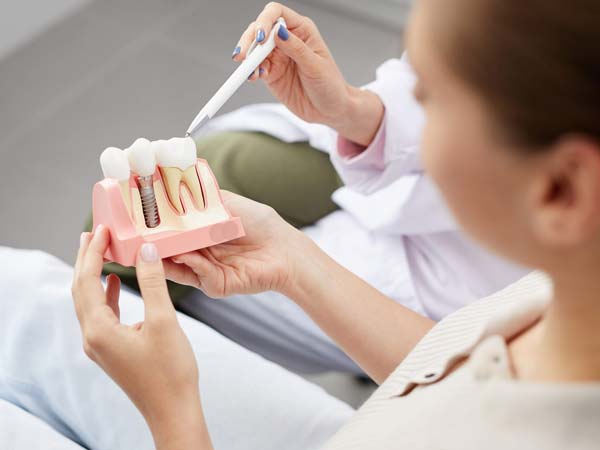
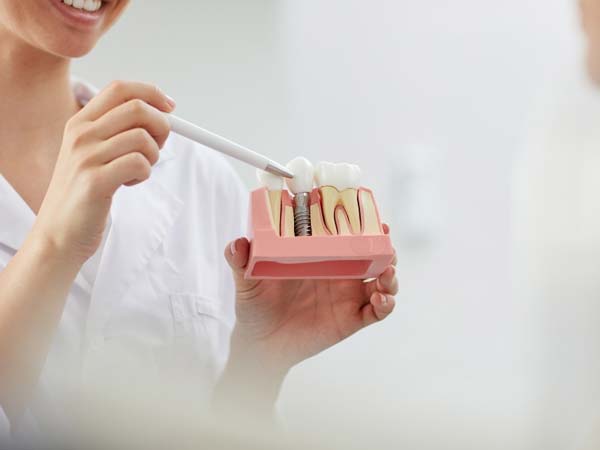
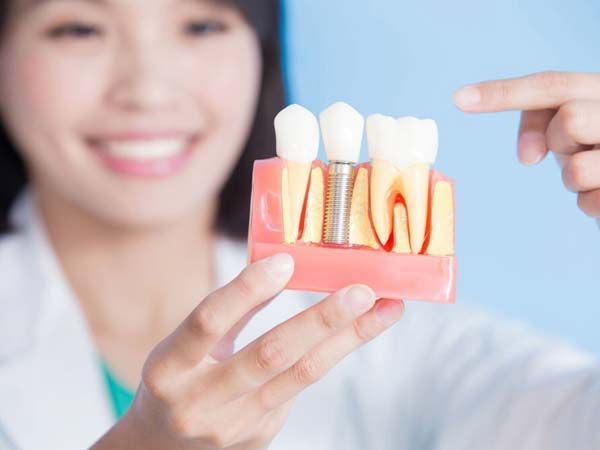
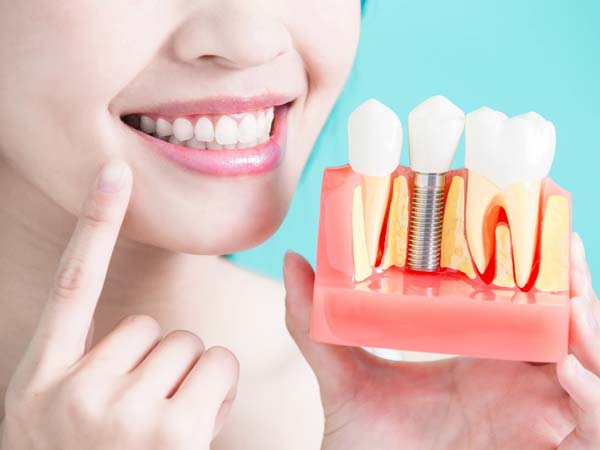
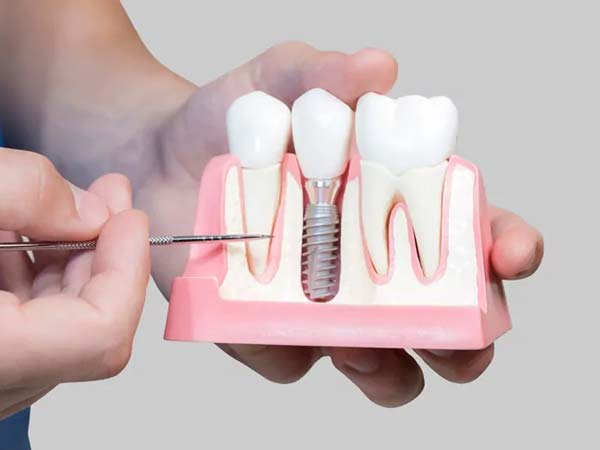
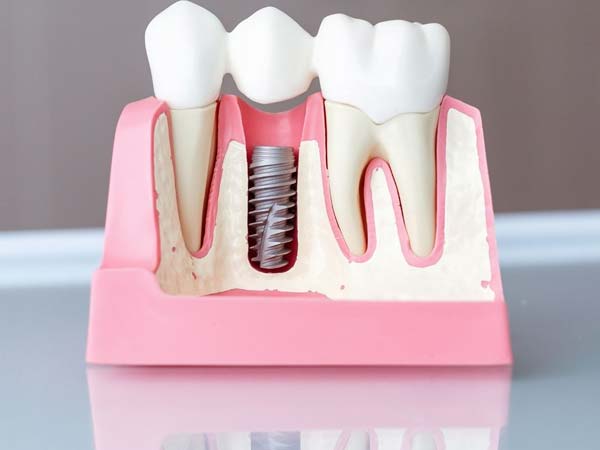
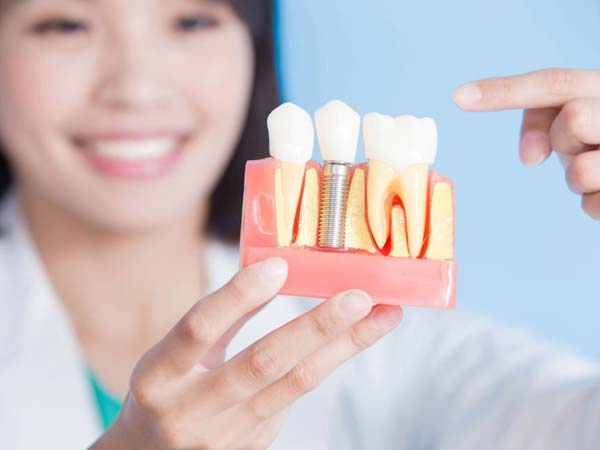
- Dental Implant Placement: Periodontists are extensively trained in the placement and maintenance of dental implants. They assess the suitability of dental implants as a replacement for missing teeth and perform the surgical procedures necessary for implant placement. Dental implants provide a stable and long-lasting solution for tooth replacement.
- Management of Complex Cases: Periodontists handle complex cases involving severe gum diseases or conditions that require specialized care. They collaborate with other dental specialists to develop comprehensive treatment plans and provide optimal care for patients with advanced periodontal issues.
Common Services Provided by Periodontists:
- Comprehensive Periodontal Evaluation: Periodontists conduct thorough examinations of the gums, teeth, and surrounding tissues to assess their health. They evaluate gum attachment levels, measure pocket depths, and assess bone density through X-rays to diagnose gum diseases accurately.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This non-surgical procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. It helps eliminate bacteria, reduce inflammation, and smooth the tooth roots to promote gum reattachment and prevent further progression of gum disease.
- Gum Grafting: In cases of gum recession, where the gum tissue has pulled away from the tooth roots, periodontists perform gum grafting procedures. This involves taking tissue from another area of the mouth or using synthetic materials to cover exposed tooth roots and restore a healthy gumline.
- Dental Implant Placement and Maintenance: Periodontists specialize in dental implant procedures, including implant placement, bone grafting, and implant restoration. They ensure proper integration of the implant with the jawbone and provide ongoing maintenance and care for long-term implant success.
Maintaining Healthy Gums:
In addition to professional periodontal care, maintaining healthy gums requires a consistent oral hygiene routine at home. This includes:
- Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline.
- Using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial growth and freshen breath.
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting sugary snacks and beverages.
Regular visits to a periodontist and practicing good oral hygiene habits are essential for preventing gum diseases, maintaining healthy gums, and preserving the longevity of your teeth.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What are the signs of gum disease? Common signs of gum disease include red, swollen, or tender gums, bleeding gums during brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, receding gums, and loose or shifting teeth. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to schedule an appointment with a periodontist for evaluation and treatment.
- Is gum disease reversible? Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is reversible with proper dental care and regular professional cleanings. However, advanced periodontitis, characterized by significant gum and bone damage, is not reversible but can be managed to prevent further progression.
- How often should I visit a periodontist? The frequency of visits to a periodontist depends on your specific needs and the health of your gums. In general, individuals with a history of gum disease or other periodontal concerns may require more frequent visits, while those with healthy gums can schedule regular check-ups every six to twelve months.
- Does gum disease have any systemic health implications? Yes, gum disease has been linked to several systemic health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory diseases, and complications during pregnancy. Maintaining healthy gums through periodontal care contributes to overall well-being and reduces the risk of developing these systemic health issues.
- Can I prevent gum disease at home? While professional periodontal care is crucial, practicing good oral hygiene habits at home is equally important. By brushing and flossing diligently, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco use, you can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease and maintain optimal oral health.